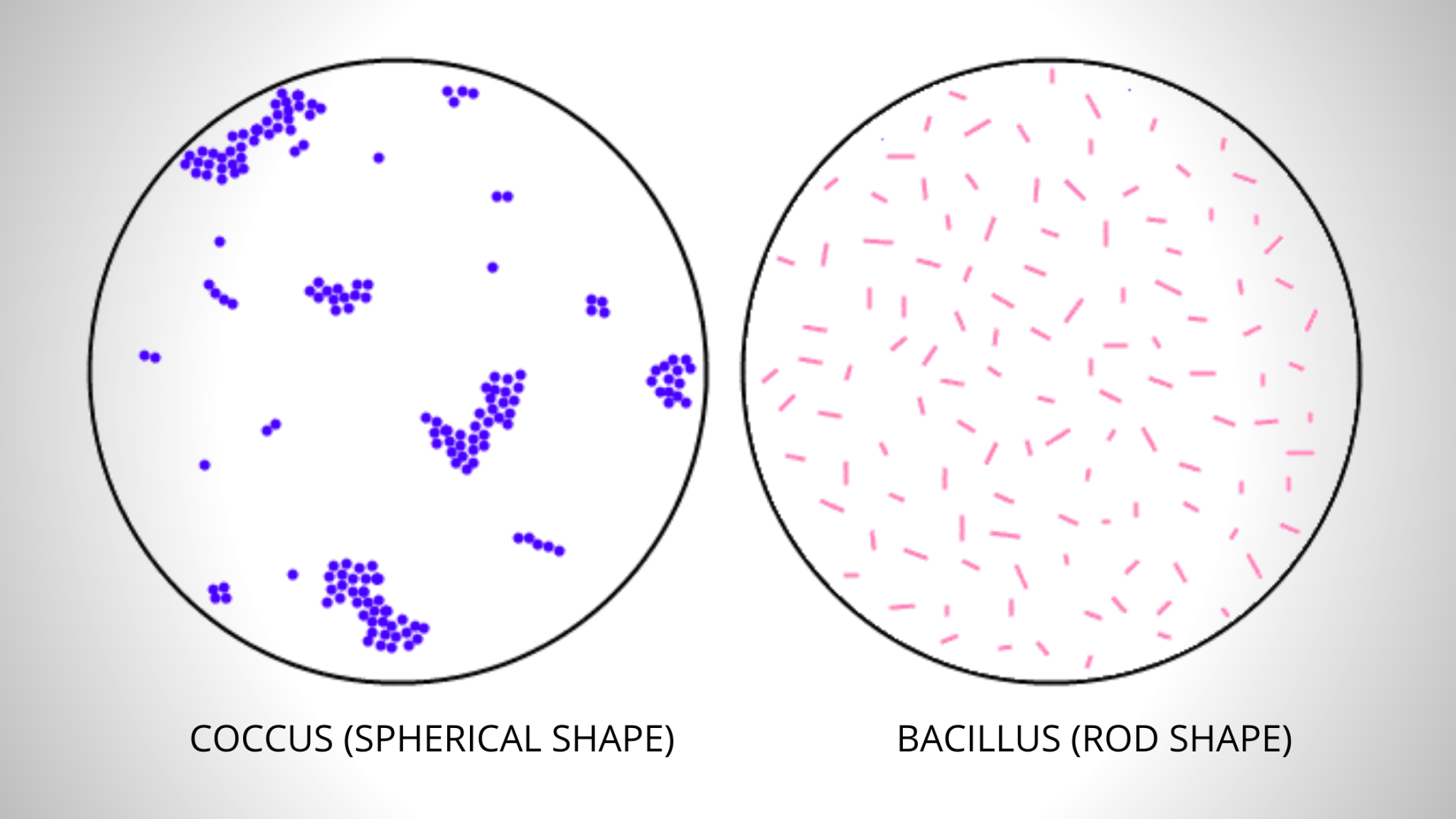
Simple Staining Procedure, Principle, Result
In a simple stain, a bacterial smear is stained with a solution of a single dye that stains all cells the same color without differentiation of cell types or structures. The single dye used here is methylene blue, a basic stain. Basic stains, having a positive charge, bind strongly to negatively charged cell components such as bacterial nucleic.
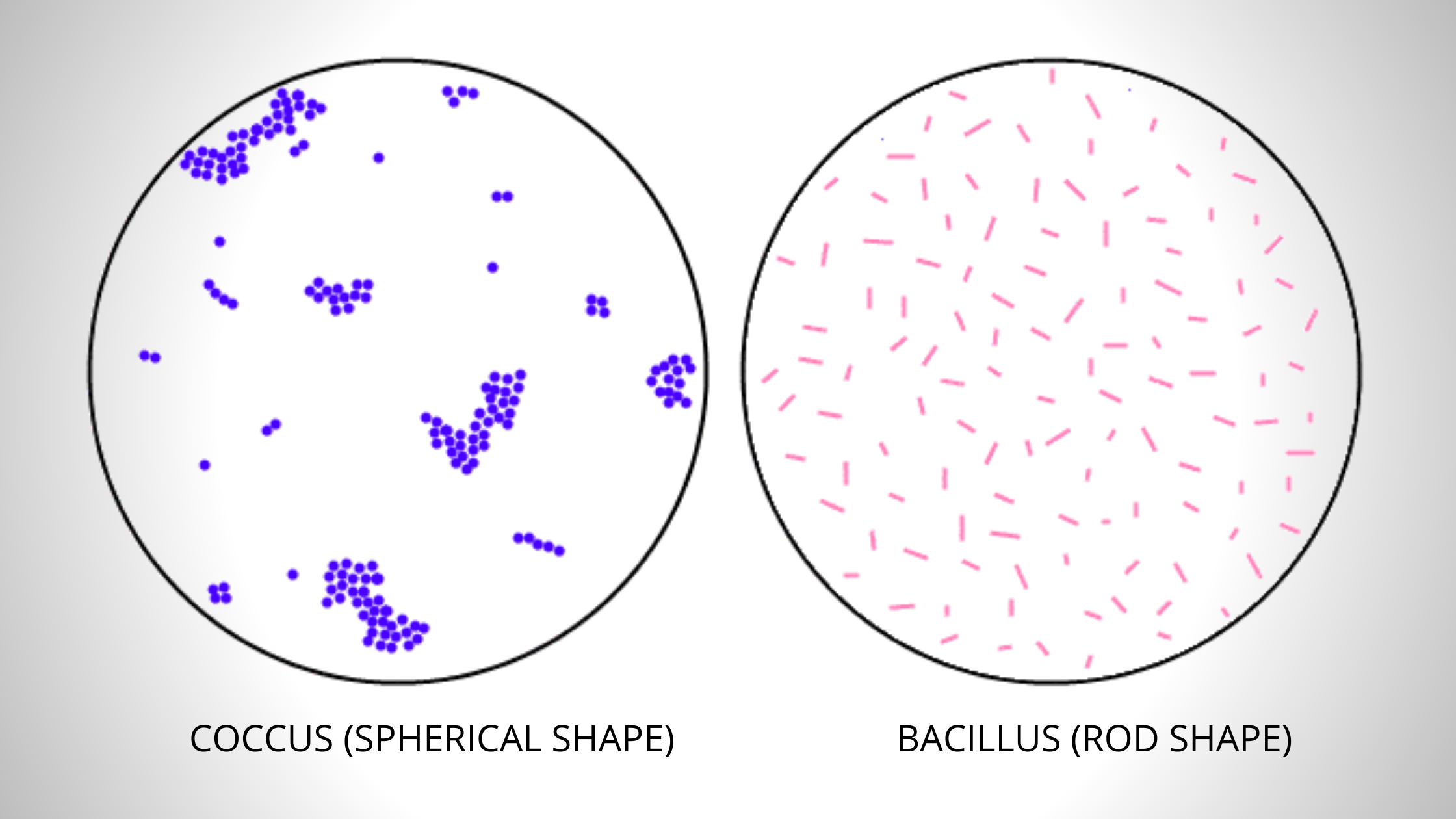
Simple Staining Procedure, Principle, Result
Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top five types of Staining. The types are: 1. Simple Staining 2. Differential Staining 3. Gram Staining 4. Acid Fast Staining 5. Endospore Staining. Staining Type # 1. Simple Staining: Colouration of microorganisms by applying single dye to a fixed smear is termed simple staining.

Gram staining procedure Microbiology, Medical laboratory technician, Medical laboratory science
Simple staining involves directly staining the bacterial cell with a positively charged dye in order to see bacterial detail, in contrast to negative staining where the bacteria remain unstained against a dark background.
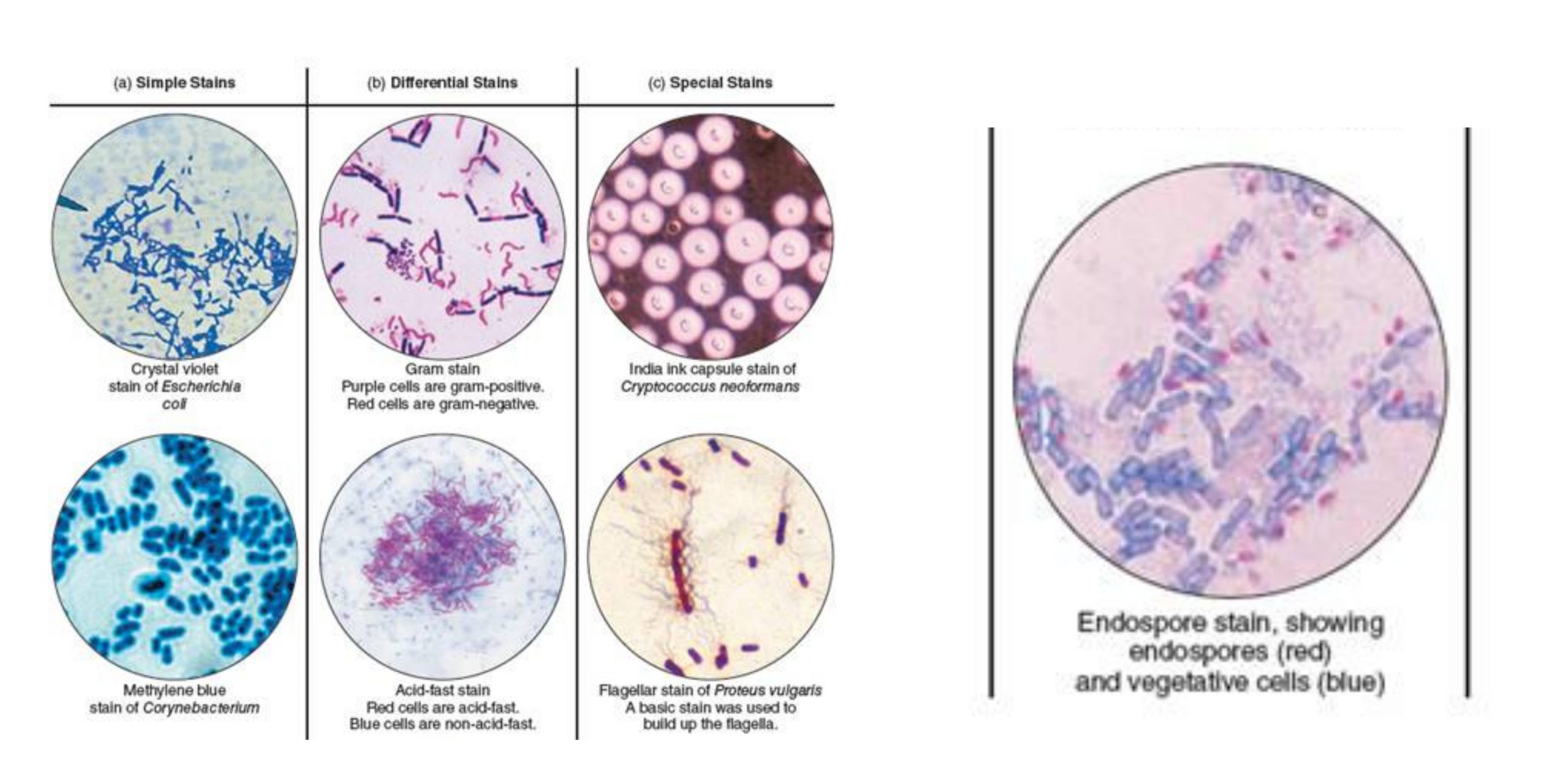
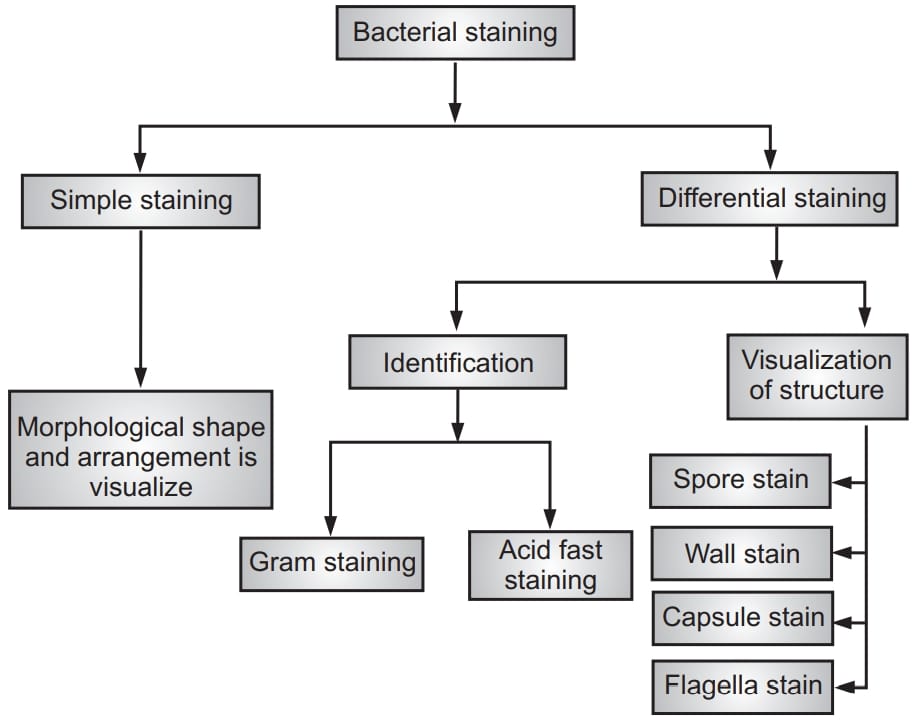
Types of Staining Techniques
Conclusion Definition of Simple Staining Simple staining is defined as one of the ordinaries yet the popular method used to elucidate the bacterial size, shape and arrangement to differentiate the various bacteria groups. It stains the bacterial cell uniformly and thus increases the visibility of an organism.

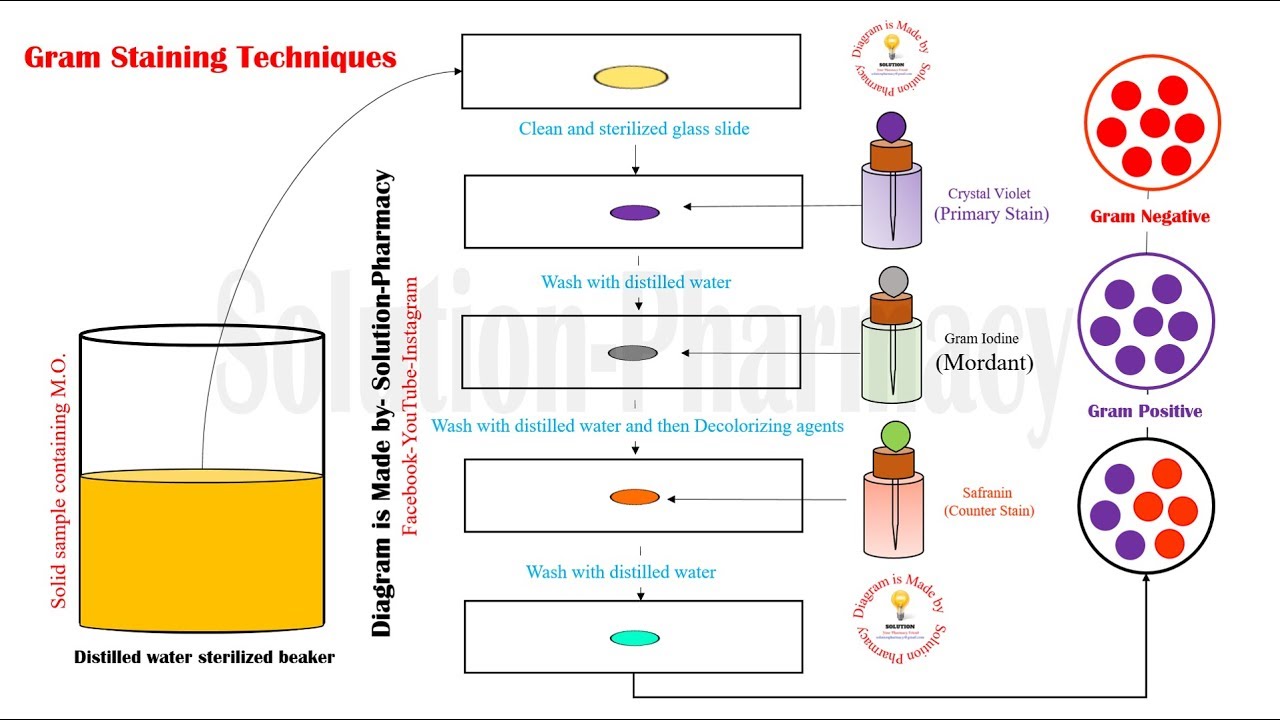
Gram Staining Principle Procedure and Results
Article Joint by ADVERTISEMENTS: The following credits highlight to top five types away Staining. The types are: 1. Unsophisticated Dyeing 2. Differential Staining 3. Gram Staining 4. Acid Fast Staining 5. Endospore Dye. Staining Type # 1. Simple Staining: Colouration out human over applying unique dye to an fixed smear is termed easy staining.

Gram Staining Principle, Procedure and Results Learn Microbiology Online Medical laboratory
Table 1: Summary of some common differential stains used in microbiology. The Gram stain uses the following dyes/reagents: crystal violet, Gram's iodine, ethanol, and safranin. The Gram stain distinguishes cells by cell wall type (Gram-positive or Gram negative). Gram-positive cells stain purple/violet.
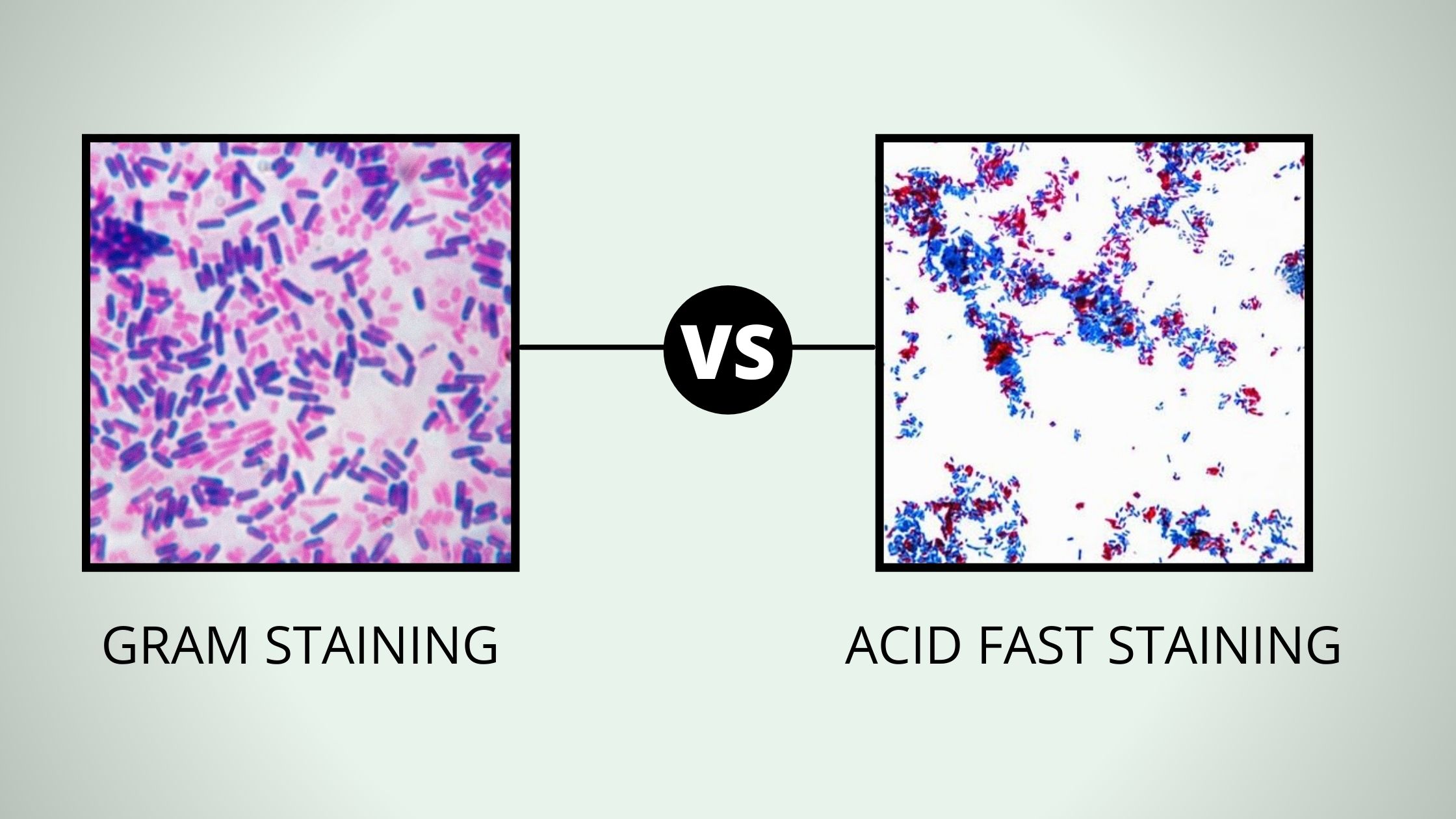
Comparison Between Gram Stain and Acid Fast
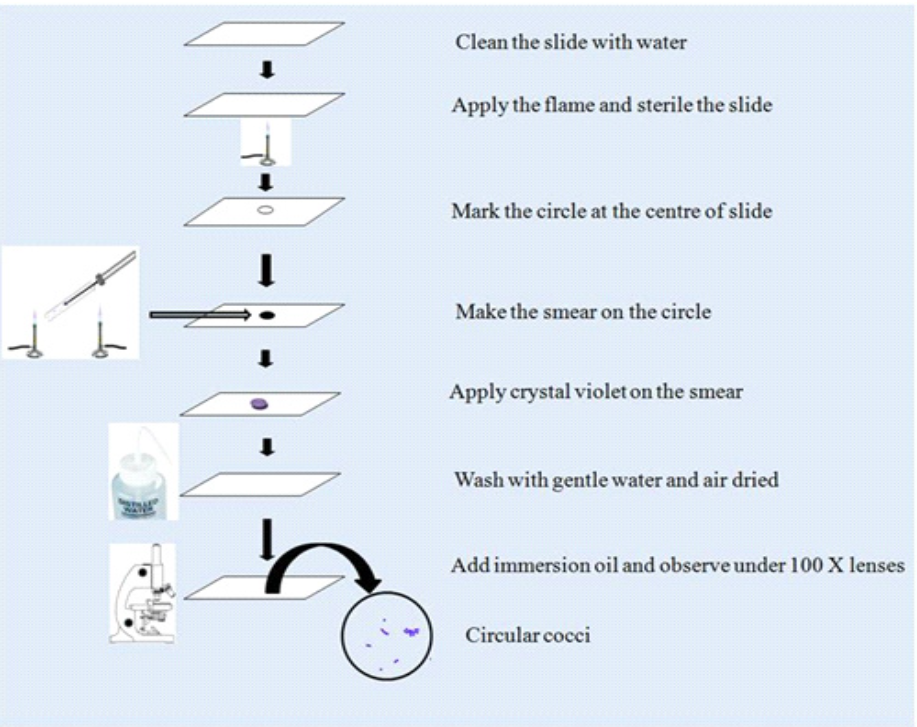
Grip the microscope slide in wood clip over a waste container bucket. Add methylene blue stain to the heat-fixed smear. There is no reason to cover the entire slide with stain. Just make sure to cover the smear with stain. Set a timer for 1.5 or 2 minutes. The stain will remain on the smear during this time.
Microbiology Mania Gram Staining, Including Simple Staining Method {Lab 3 May 14, 2015}
Principle: Simple staining uses single basic dyes such as crystal violet which is dissolved in a solvent and applied to the microorganisms. The microorganisms give the colour characteristics of the staining solution. Because of which shape and size of microorganisms can be determined. Requirements:
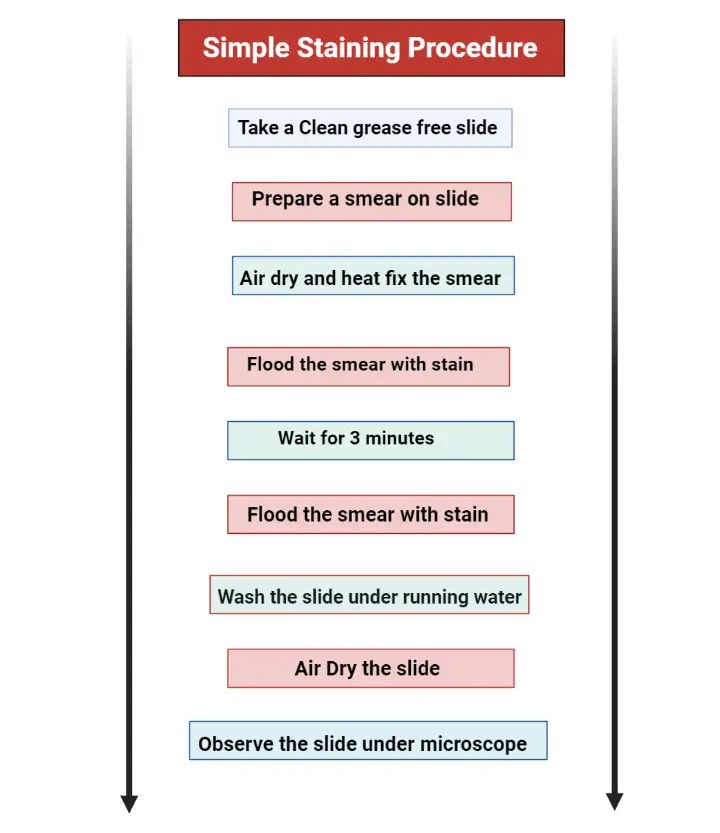
Simple Staining Procedure, Principle, Result
In a simple stain, a bacterial smear is stained with a solution of a single dye that stains all cells the same color without differentiation of cell types or structures. The single dye used here in our lab is methylene blue, a basic stain. Basic stains, having a positive charge, bind strongly to negatively charged cell components such as.

Simple staining Procedure and its Mechanism Microbiology with Sumi YouTube
A simple stain will generally make all of the organisms in a sample appear to be the same color, even if the sample contains more than one type of organism. In contrast, differential staining distinguishes organisms based on their interactions with multiple stains. In other words, two organisms in a differentially stained sample may appear to.
Identification of Bacteria Using Staining Techniques
The purpose of simple staining is to elucidate the morphology and arrangement of bacterial cells. The most commonly used basic stains are methylene blue, crystal violet, and carbol fuchsin. Reagents and Equipment's for Simple Staining
Gram Staining Technique = Simple Explanation Via Animated Presentation (HINDI) By Solution
2.3 KINDS OF STAINS Stains are classified as zSimple stain zDifferential stain zStructural or special stains Simple Staining The staining process involves immersing the sample (before or after fixation and mounting) in dye solution, followed by rinsing and observation. Many dyes, however, require the use of a mordant, a chemical compound that.
Simple Staining Procedure. Download Scientific Diagram
Grasp the slide with a slide holder and pass the smears through the upper part of a flame at least 2-3 times. Avoid overheating the slide. Place the slide on the metal stain rack over the sink. Cover the smears with the stain using the following times: Crystal violet: stain for 30 to 60 seconds.
Simple Staining Principle, Procedure, Results and Application Biology Ease
A simple stain in microbiology is the addition of a cationic or positively charged dye to a slide. This dye then stains the clear or translucent cells on the slide or sample. By doing so, a.

Microbial Staining= Simple Staining Gram Staining Acid Fast Staining Staining Technique
True to its name, the simple stain is a very simple staining procedure involving a single stain solution. Any basic dye, such as methylene blue, safranin, or crystal violet, can be used to color the bacterial cells. These stains will readily give up a hydroxide ion or accept a hydrogen ion, which leaves the stain positively charged.

Medical technology, Microbiology, Medical laboratory science
Simple staining technique uses a single stain to visualize the bacteria, which produces a distinctive contrast between the organism and its background.